




Peanut oil is light yellow and transparent, with clear color, fragrant smell and delicious taste. It is a relatively easy-to-digest edible oil. The unsaturated fatty acid content in peanut oil is more than 80% (including oleic acid 41.2%, linoleic acid 37.6%), and it also contains 19.9% of saturated fatty acids such as palmitic acid, stearic acid, and arachidic acid.

There are two methods for producing peanut oil: pressing and pre-pressing. Pressing is the process of mechanically extracting oil from peanuts using an oil press. Pre-pressing is the process of extracting oil from peanuts using an organic solvent after some of the oil has been extracted using a pre-press.
The pressing process includes cleaning, shelling, crushing, flaking, cooking, pre-pressing and pressing. After peanuts are picked or purchased from suppliers, some impurities such as stones, branches, metals, etc. are mixed in. In order to prevent damage to the equipment, vibrating screens, stone removers, magnetic separators, etc. are usually used to remove impurities. After removing impurities, shelling is carried out to increase the oil yield. Crushing makes the peanut kernel smaller in size and larger in surface area. Flaking and cooking can adjust the moisture and temperature of peanuts to make them suitable for pressing. This series of processes is collectively referred to as peanut pretreatment. After pretreatment, the treated peanuts are pressed for the second time using a pre-pressing machine and a press to reduce the loss of peanut oil and obtain more peanut oil.

The pre-pressing and leaching method also requires pre-treatment of peanuts, cleaning impurities in peanuts, adjusting the moisture and temperature of peanuts, and improving the production efficiency of peanut oil. The pre-treated peanuts are pre-pressed with a pre-pressing machine to obtain crude oil and cake. The residual oil rate in the cake is about 7%, and the oil in the cake needs to be extracted by leaching equipment. The leaching equipment generally includes four systems: leaching oil system, wet meal desolventizing system, mixed oil processing system and solvent recovery system. The residual oil rate in the cake after leaching is less than 1%.
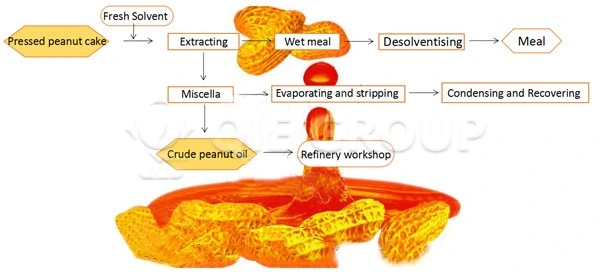
The crude oil obtained by pressing contains impurities such as free fatty acids, phospholipids, pigments, and odorous substances, which need to be removed through refining technology to meet national edible oil standards.
Degumming : Add hot water or dilute alkaline solution to the crude oil to make phospholipids and other colloids absorb water, expand and condense, and then remove phospholipids and other colloid-soluble impurities by centrifugation.
Deacidification : Add caustic soda solution to the crude oil to neutralize the free fatty acids to form soap stock, and then centrifuge to remove the alkali.
Decolorization : Remove pigments. Adsorption decolorization uses adsorbents such as activated clay and activated carbon to remove pigments such as chlorophyll and carotene.
Deodorization : Use high temperature (240-260℃) and vacuum (≤0.001MPa) steam distillation to remove odors and remove malodorous substances such as free fatty acids and aldehydes.

The above is the process of peanut oil production line. The configuration of peanut oil production line needs to consider factors such as the scale of the investor's plant, output, quality, budget, etc., and provide equipment configuration plan and quotation according to needs. QIE manufacturer has focused on the research and development and production of oil machinery for many years, and the equipment produced is of high quality and preferential price. The equipment types and models are complete, providing customized services for customers, and the production line can be configured according to needs.